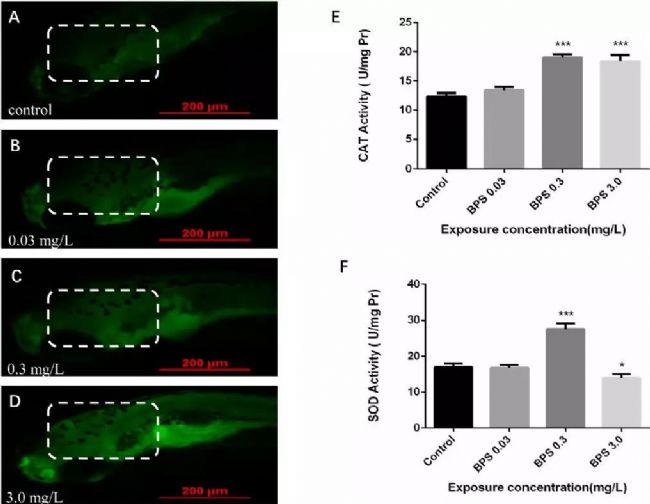
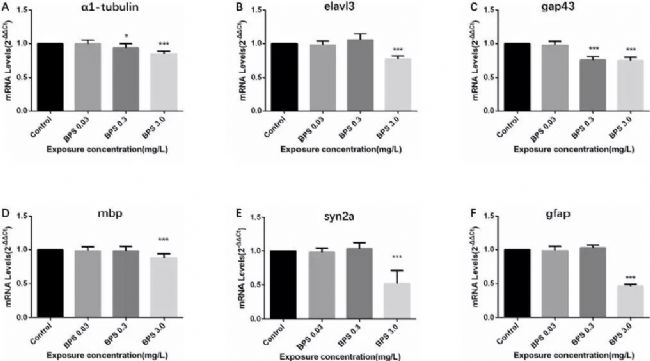
Bisphenol A (BPA) is present in many products such as food packaging and plastic products, and there is increasing evidence that it has endocrine disrupting functions and is harmful to human health. Some structurally similar alternatives such as bisphenol S (BPS) (Rochester and Bolden, 2015; Wu et al., 2018b; Zhao et al., 2018) are widely used in various industrial applications, such as cleaning agents, Electroplated portion of phenolic resin and developer of thermal paper (Liao et al., 2012b). Bisphenol S (BPS), as a substitute for bisphenol A (BPA), has been widely used in the production and manufacture of everyday consumer goods. Since the structure of BPS is similar to BPA and has a wide range of uses, the safety of BPS has been receiving much attention. Some scholars have conducted relevant research on BPS: 1. In vitro and in vivo exposure studies, BPS and its metabolites have been shown to interfere with the endocrine system (Wu et al., 2018a); 2. A 2015 study showed that BPS interferes with sex hormone levels. 3. Acute low-dose BPA or BPS exposure can alter zebrafish hypothalamic development, leading to hyperactivity (Kinch et al., 2015), while long-term exposure to BPS can lead to impaired retinal structure in male zebrafish and reduced traceability. A series of studies have shown that BPS may produce health hazards similar to BPA (Rochester and Bolden, 2015). The impact of BPS on the nervous system is still unclear, including the impact on retinal structure and behavioral activities. So what does the specific research look like? Please see the specific introduction below. Main findings The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of BPS toxicity on neurodevelopment and other aspects, and to explore its underlying mechanisms using fish and human disease models. By detecting zebrafish behavior, apoptosis (AO staining), oxidation reaction, gene expression, histomorphology and immunofluorescence, this conclusion was reached: BPS may inhibit the expression level of neurodevelopmental genes by increasing oxidative stress. Thereby affecting the activity of zebrafish juveniles and changing their retinal structure. These results combine to demonstrate for the first time the developmental neurotoxicity of BPS in the aquatic system, providing new ideas for the intervention pathway of BPS-induced neurotoxicity. The main data research results are detailed below: 02 Effect of BPS on behavioral activities of zebrafish juveniles after 6 days of fertilization Figure 02 shows the results of the freestyle test. It can be seen from Fig. 02 that the total distance and movement speed of zebrafish juvenile fish activity decreased with different concentrations of BPS (decreased/decreased with the increase of BPS concentration). There were significant differences between the 0.3 mg/L and 3.0 mg/L doses compared to the control group. At the same time, the total distance and average speed of movement of zebrafish juveniles in the positive control group also decreased. These results indicate that BPS can lead to a reduction in zebrafish behavioral activities. After the results of BPS causing a decrease in zebrafish behavior, in view of previous studies showing that excessive oxidative stress affects zebrafish movement behavior (Chen et al., 2017), the researchers explored whether BPS would Causes oxidative stress. 03 Changes in CAT and SOD activity and brain cell apoptosis after zebrafish fertilization for 6 days Figure 03 shows changes in CAT and SOD activity and brain cell apoptosis after 6 days of zebrafish fertilization. As can be seen from Figure 03, zebrafish CAT activity increased significantly at BPS concentrations of 0.3 mg/L and 3.0 mg/L compared to the control group (Fig. 03E); in addition, when the BPS concentration was 0.3 mg/L, Compared to the control group, zebrafish SOD activity reached its highest value (Fig. 03F). However, when the BPS concentration reached its maximum value (3.0 mg/L), SOD activity decreased significantly (Fig. 03F). The results showed that the SOD enzyme was continuously depleted or the activity was reduced, that is, BPS significantly increased the oxidative stress response of zebrafish. After verifying this result (BPS significantly enhanced oxidative stress in zebrafish), the researchers used AO staining to investigate the apoptosis of zebrafish juveniles induced by BPS. As can be seen from Fig. 03, there was no obvious apoptotic cells in the brain of zebrafish juveniles compared with the control group, including BPS concentration of 0.03 mg/L (Fig. 03A, B); however, the BPS concentration was 0.3 mg/ Significant apoptosis was observed at L and 3.0 mg/L (Fig. 03C, D). A more important finding is the severe radiation in the zebrafish brain. This suggests that BPS may cause brain damage in zebrafish juveniles. 04 Gene expression of zebrafish juveniles after BPS administration After BPS administration of zebrafish juveniles 6 days after fertilization, the researchers evaluated six genes related to neurodevelopment ((a1-tubulin, elavl3, gap43, mbp, syn2a, and gfap)). As can be seen from Fig. 04, the gene level of the high-concentration BPS group was significantly decreased as compared with the control group. These data indicate that BPS may affect neurodevelopment. Previous studies have shown that BPS can damage the retinal structure of zebrafish (Liu et al., 2017a). In order to further explore this mechanism of action, the researchers also explored whether BPS would alter the retina of zebrafish juveniles. structure. 05 Retinal structure changes of zebrafish juveniles (control group and BPS group) It can be seen from Fig. 05 that the control group zebrafish retina has a complete structural structure with no significant changes, which are as follows: regular morphology, 5 complete typical thin layers. However, when zebrafish were exposed to BPS at a concentration of 0.3 mg/L to 3.0 mg/L, the morphology of the retina began to be abnormal and a blank area began to appear in the RPE (Fig. 05B-D). As the BPS concentration increases, the blank area increases (as shown in the white arrow portion of Fig. 05). In addition, compared with the control group, the ganglion cells of the BPS group became sparse (as shown in the white triangle in Fig. 05D). After the onset of abnormalities in the retina morphology was determined, the researchers performed immunohistochemical studies using GAP43 protein (protein expression in the eye) (Kaneda et al., 2010). In the retina of zebra juveniles, GAP43 protein is used as a good biochemical indicator for monitoring the entire process of optic nerve regeneration. As shown in Figure 05E-H. At the concentration of 0.3 mg/L-3.0 mg/L BPS, the expression of GAP43 protein was significantly decreased. The above results are consistent with the results of gene expression. The study is a systematic study that illustrates the underlying mechanisms of developmental neurotoxicity and BPS-mediated neurotoxicity. Studies have shown that exercise behavior testing is an effective method for detecting neurotoxicity of drugs and environmental chemicals (Sano et al., 2016), which is also an advantage of Noldus's behavioral research tools, which enables quantitative observation and analysis of behavioral activities. Taken together, the results of this study indicate that early exposure to BPS has an effect on motility, brain damage, CAT and SOD activity, pathological changes, and neuronal gene transcription in zebra juveniles, suggesting that BPS may potentially interfere with nervous system development. . After reading it, it must be very clear that the original substitute is not really safe and non-toxic. On the necessity of conducting research! ! ! Of course, research tools are also extremely important. The above is the main research results of the research, detailed literature and content, if you want to know more, please contact us for relevant information. references: Chen, Q., Gundlach, M., Yang, S., Jiang, J., Velki, M., Yin, D., Hollert, H., 2017. Quantitative investigation of the mechanisms of microplastics and nanoplasticstoward zebrafish larvaelocomotor activity. Sci. Total Environ. 584e585, 1022e1031. Jie Gu,Jiayao Zhang, Yaoyao Chen, Hongye Wang, Min Guo,Lei Wang, Zhen Wang, ShengminWu, Lili Shi, Aihua Gu, Guixiang Ji.,2018. Neurobehavioral effects of bisphenolS exposure in early life stages of zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio ). Kinch, CD, Ibhazehiebo, K., Jeong, JH, Habibi, HR, Kurrasch, DM, 2015. Low-dose exposure to bisphenol A and replacement bisphenol S induces precocioushy-pothalamic neurogenesis in embryonic zebrafish. Proceed. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 112, 1475e1480. Liao, C., Liu, F., Kannan, K., 2012b. Bisphenol s, a new bisphenol analogue, in paperproducts and currency bills and its association with bisphenol a residues. En-viron. Sci. Technol. 46, 6515. Liu, W., Zhang, X., Wei, P., Tian, ​​H., Wang, W., Ru, S., 2017a. Long-term exposure tobisphenol S damages the visual system and reduces the tracking capability ofmale zebrafish ( Daniorerio). J. Appl. Toxicol.: JAT 38 (2), 248e258. Rochester, JR, Bolden, AL, 2015. Bisphenol S and F: a systematic review and comparison of the hormonal activity of bisphenol a substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect.123, 643e650. Sano, K., Isobe, T., Yang, J., Win-Shwe, TT, Yoshikane, M., Nakayama, SF, Kawashima, T., Suzuki, G., Hashimoto, S., Nohara, K., Tohyama, C., Maekawa, F., 2016. Inutero and lactational exposure to acetamiprid induces abnormalities insocio-sexual and anxiety-related behaviors of male mice. Front. Neurosci. 10,228. Wu, LH, Zhang, XM, Wang, F., Gao, CJ, Chen, D., Palumbo, JR, Guo, Y., Zeng, EY, 2018b. Occurrence of bisphenol S in the environment and implications for humanexposure: a Short review. Sci. Total Environ. 615, 87e98. Wu, LH, Zhang, XM, Wang, F., Gao, CJ, Chen, D., Palumbo, JR, Guo, Y., Zeng, EY, 2018a. Occurrence of bisphenol S in the environment and implications for humanexposure: a Short review. Sci. Total Environ. 615, 87e98. Zhao, F., Jiang, G., Wei, P., Wang, H., Ru, S., 2018. Bisphenol S exposure impairsglucose homeostasis in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 147, 794e802. Gauze Swabs,Gauze Cotton Swab,Sterile Gauze Swabs,Absorbent Gauze Swab Xinxiang Huaxi Sanitary Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.huaximedical.com
Environment and human health are currently the most concerned. Bisphenol A ( BPA ) is present in all aspects of consumer products in daily life. It is widely used in the packaging of canned foods and beverages, sealants and glasses for bottles, water bottles and dental fillings. Tablets and hundreds of other daily necessities are being manufactured.
However, bisphenol A is toxic . Prolonged intake and absorption can be harmful to liver function and kidney function, and it can reduce the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Studies have shown that bisphenol A is associated with heart disease, diabetes, and abnormal liver function in adults. The chemical substance bisphenol A in plastic products can induce heart disease. It is an endocrine disruptor that mimics the body's own hormones and can have a negative impact on health. BPA has been banned in the United States, the European Union, Canada and Norway.
In order to respond to and reduce consumers' concerns about safety, many plastic products on the market are also labeled with “BPA-free†to promote safe use.
It is also because of the similar chemical structure and the toxicity of BPA that BPS has gradually become a substitute for BPA . But regarding alternatives, I think everyone has doubts in their hearts: Is it really safe to have no bisphenol A? Is the alternative BPS really completely non-toxic? Does it have an impact on human health?
It is well known that zebrafish is a widely accepted experimental research model because of its characteristics similar to human genes. Recently, the Key Research Laboratory of the Institute of Toxicology of Nanjing Medical University, the Key Laboratory of Toxicology of the School of Public Health of Nanjing Medical University, and the Nanjing Institute of Environmental Protection have used DanuoVision and EthoVision of Noldus , namely zebrafish behavior trajectory tracking and animals. The trajectory tracking system was used to observe and analyze the zebrafish juveniles, and the important effects of BPS on the early neurodevelopment, retinal structure and behavior of zebrafish juveniles were discussed. 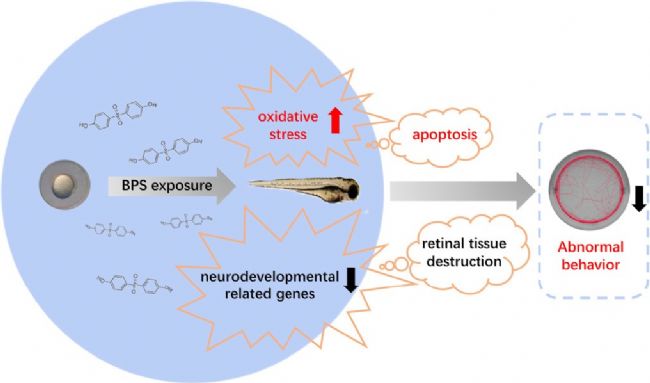
Research Background 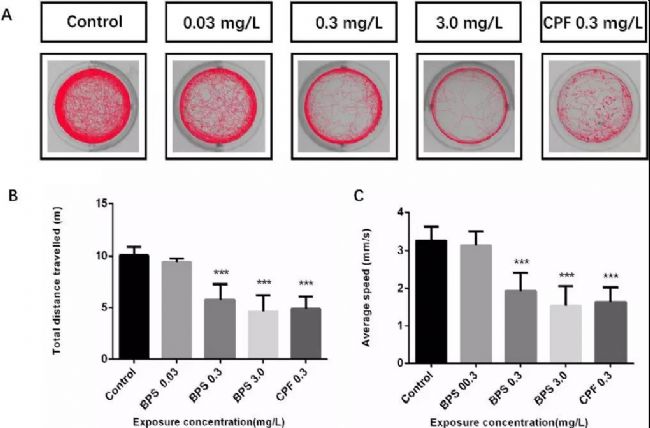

 .
.
Study on the Mechanism of the Effects of Bisphenol S (BPS) Toxicity on Neurodevelopment and Other Aspects
Is ubiquitous bisphenol S (BPS) really safe and non-toxic?