Xiaoao classroom is coming again! I. Introduction For the purpose of biomacromolecule detection, the drug concentration and biomacromolecular markers of blood samples in animal experiments and clinical experiments are quantitatively detected during pharmacodynamic drug evaluation ; For the purpose of affinity determination, the affinity of the antibody relative to the target antigen is detected during the mass analysis ; For the purpose of affinity screening, in the process of antibody discovery , the affinity of the secreted antibody of the hybridoma cell clone supernatant relative to the target antigen is differentiated. For different purposes, you need to select different characteristic reagent supplies. The parasitic polymorphism is wonderful in the world, and the development of ELISA methodology is also a truth. This article is one of the major examples of the development of the ELISA method - the specific experimental program for the development of quantitative methods for the detection of biological macromolecules, suitable for all the primary contact ELISA method technology and interested in the development of ELISA method. How wonderful, and look down: Second, the type and structure of ELISA quantitative methods The indirect method is also called the competition law, and the direct method is also called the double-anti-sandwich method. Today, we focus on introducing direct law to everyone. The direct method uses quantitative antigen as an example: First, an antibody with a strong affinity for an antigen is immobilized on an enzyme-labeled plate, an antigen standard/sample reaction is added, an antibody having a strong affinity for the antigen is added, and horseradish catalase HRP/alkaline is coupled. The enzyme-linked antibody reaction of the phosphatase AP is finally added to the substrate corresponding to the enzyme, and the unreacted reagent component in the reaction system is removed by washing. Thus, the signal size is positively correlated with the concentration of the antigen. As the reaction proceeds, the components immobilized on the plate are converted from antibodies to antibody-antigens, and finally to antibody-antigen-enzyme-linked antibodies. The antigen to be tested is in two antibodies. Between, so also known as double-anti-sandwich method. The double-anti-sandwich method has a key point: the substance to be detected (such as the antigen) must provide two binding sites for the coated antibody and the enzyme-linked antibody, and the two sites can be two or more identical structural sites on the antigen. It can also be a different structural site. In general, Elisa's framework consists of standards, internal controls, blank controls, matrix controls, and samples to be tested. Standard Depending on the specific application direction of the experiment, the standard can be a known concentration of international/national standard or a commercially known protein molecule of known concentration, or it can be self-made by other means of quantification (such as UV absorption quantification). High protein molecules. Standards are typically 7-8 concentration points and are fitted to the appropriate concentration-signal dose curve as a standard curve for quantification of internal controls and samples. Internal control Among them, the internal control product is a long-term, independently packaged, specific concentration (high, medium, low) standard, which is the quality of the monitoring ELISA experiment in a single experiment and the transition bridge of different batches of standard products in the long-term application process. . Blank control The blank control is a standard solution without a standard, and the matrix control is a sample solution containing no sample. The two may be the same component or different components, and need to be differentiated according to the specific conditions of the experiment. Confirmation of non-specific cross-reactivity in the ELISA system. Third, ELISA experiment: Is your consumable reagent selected correctly? The key to the development of a successful ELISA method is the selection and matching of reagent consumables used in ELISA experiments. Knowledge of the characteristics and diversity of reagent consumables helps to develop a high-quality ELISA method for finding the right combination of different experimental needs. The enzyme-labeled plates available on the market are basically polystyrene, and the company with a full line of products has various chemical modifications to polystyrene materials with different characteristics relative to the coated proteins. The specifications of the general enzyme-labeled plates are classified according to the high binding and medium binding dimensions. However, based on years of experience, the author will trust the enzyme-labeled plates with the type and characteristics of the enzyme-labeled plates in four levels: hydrophilic, weakly hydrophilic, untreated and hydrophobic. In general, the enzyme-labeled plate is hydrophilic to hydrophobic, and the binding to the protein will gradually weaken, which brings three effects: At the same concentration of protein coating, the binding ability of the material with weaker binding ability can immobilize more protein on the enzyme-labeled plate because the maximum adsorbed antibody amount of the single-hole hydrophilic plate is 220 ng, while the hydrophobic plate is only 100 ng. From hydrophilic to hydrophobic, the adsorption efficiency of the plate on the coated protein is improved, and its ability to non-specifically adsorb the sample protein, other proteins in the sample solution and the enzyme-linked antibody during the ELISA reaction is also increased, resulting in non- Specific signal. The coated protein acts as a macromolecule on a surface of the enzyme-labeled plate. The surface of the coated protein on the different enzyme-labeled plates is not random and uniform in most people's imagination. It has obvious bias and leads to different characteristics. On the enzyme-labeled plate, the contact surface of the coated protein and the enzyme-labeled plate is different, thereby causing different sites to be shielded. If this site happens to be the site that binds to the test sample, the sample will therefore not be detected. Therefore, a laboratory that focuses on the development of diverse ELISA methods should be prepared with a variety of different specifications of the enzyme plate. The commonly used coating solution is PBS (pH 7.4) or sodium carbonate-sodium bicarbonate solution pH 9.6. The pH and ion concentration will have certain influence on the coating efficiency. It needs to be analyzed according to the characteristics of the coated protein. After the coating, the protein solution is not adsorbed on the enzyme label plate, and most of the protein remains in the solution after the coating is completed. In the literature, there are cases in which the protein is dissolved in the coating solution and vacuumed to adsorb the coated protein on the enzyme-labeled plate at a higher density. Commonly used blocking agents are 3% BSA (w/v), 5% skim milk powder (w/v) and the like. The function of the blocking solution is to cover the space outside the position occupied by the enzyme-labeled plate to prevent direct non-specific adsorption of the plate by subsequent samples or other substances in the sample, enzyme-linked antibodies, and the like. According to the author's many years of practical experience, the blocking agent can only better seal the sample solution with simple composition, but the sealing effect will be greatly reduced in the face of the more complex sample solution. Studies have shown that the blocking effect of the blocking agent is inversely proportional to the size of the blocking molecule, so if the traditional blocking agent does not have a good blocking effect, a smaller molecular weight blocking agent (such as casein) may be used. Good closure effect. In addition, special attention should be paid: If the detection system is a biotin-streptavidin system, do not use skim milk powder as a blocking agent - because the biotin in the skim milk powder will interfere with the detection system. Commonly used washing solutions are neutral buffers plus a concentration of detergent such as PBST (0.05% (V/V) Tween-20 in PBS). The diluent will be filled with a certain blocking agent component such as 0.5% BSA (W/V) in PBST. In the detection of some in vivo samples, a certain concentration of negative serum is usually added to the dilution so that samples of different dilutions have the same non-specific background. There are many types of enzyme-linked antibodies, and they can be classified into specific enzyme-linked antibodies and general-purpose enzyme-linked antibodies depending on the site of action of the antibody. A specific enzyme-linked antibody acts on an epitope of a specific protein. General-purpose enzyme-linked antibodies are often directed against the tag of the polypeptide sequence, biotin, the Fc-terminal conserved region of a particular species of antibody, and the like. Commonly used enzyme-linked antibody-labeled enzymes are mainly AP (alkaline phosphatase) and HRP (horseradish catalase). The enzyme-linked antibody can be classified into a monoclonal antibody-linked antibody and a polyclonal antibody-linked antibody according to the components of the antibody. The multi-anti-reactive component of the multi-anti-enzyme-linked antibody is generally obtained by immunizing a rabbit or a goat, and the composition is relatively complicated, and it is necessary to pay special attention to the cross-reaction with other reagents in the ELISA system. The enzyme-linked antibody can be classified into a full-length enzyme-linked antibody, a Fab fragment-enzyme-linked antibody, and an scFv-linked antibody according to the molecular weight of the antibody. The smaller the molecular weight of the enzyme-linked antibody, the more likely it is to avoid the steric hindrance of the site of action when the protein is bound to the sample protein, but it also further increases the blocking of the enzyme-linked antibody bypassing the blocking agent and non-specific with the enzyme-labeled plate. The risk of integration. The selection of the color developing solution should be in accordance with the enzyme of the enzyme-linked antibody, and it is also required to correspond to the microplate reader provided in the laboratory. If the enzyme-linked antibody is coupled with HRP (horseradish catalase), TMB coloring solution can be used to detect with a microplate reader capable of reading absorbance; Or AmplifluTM Red is a substrate that can be detected with a microplate reader that can perform fluorescence readings; or with QuantaRedADHP as a substrate, using a microplate reader that can perform chemiluminescence readings. In general, the sensitivity of the ELISA method is limited by the detection method of the substrate, and the lower limit of the signal that the chemiluminescent substrate can detect is superior to the fluorescent substrate, and is superior to the absorbance substrate. Even the commonly used TMB coloring solution, many suppliers of different color rendering strength of the coloring solution, can choose the coloring solution according to the specific conditions of the method development process. Layout description An uncoated (gray) group is added, which is necessary to confirm the non-specific adsorption of the sample to be tested or the reference substance to the plate. The sample is subjected to low, medium and high dilutions to determine the parallelism of the sample relative to the control, ie whether the sample and the control have the same immunological properties in the same ELISA system. If the signal value of the low, medium and high samples is within the reasonable quantitative range of the standard curve, the three groups of the low, medium and high samples are corrected by the dilution factor, indicating that the sample and the reference are parallel, and the parallelism is poor. This control cannot be used as a standard curve. General operating procedure 01 Preparation of the enzyme plate: Take the antibody at a concentration of 100 ug/ml, dissolve at room temperature, mix with the coating solution and dilute to 5 ug/ml according to the following steps, add 100 ml/well according to the sample layout table, and add the enzyme-labeled slats separately. (Note 1) , in which a coating solution was added as a blank for coating the antibody, and overnight at 2-8 °C. 02 Wash the plate 3 times with washing solution, pat dry, add 300 ml / hole blocking solution (Note 2) for 1 hour at room temperature; wash the plate 3 times, pat dry for use; 03 Gradient dilution of the antibody control and high , medium and low dilution of the sample (Note 3) , 100 ul/well was added to the standard dilution in a microplate. 04 Put into the Ohaus microplate shaker and set to shake at 37 ° C, 600 rpm for 1 hour; 05 Wash the plate 3 times with washing solution and pat dry; 06 The enzyme-linked antibody was diluted to the appropriate concentration (Note 4) and mixed on an Ohaus vortex mixer at 100 ul/well. 07 Placed in a microplate shaker and set to shake at 37 ° C, 600 rpm for 1 hour; 08 Wash the plate 4 times with washing solution, pat dry; 09 Take the coloring solution corresponding to the enzyme-linked antibody, take out the equilibrium to room temperature 20 minutes before use, and mix on the vortex mixer; 10 Add the color developing solution at 100 ml/well using an 8-row gun; 11 The coloring solution is allowed to stand at room temperature for 10-30 minutes (Note 5) 12 The reaction was terminated by adding a stop solution at 100 ml/well using an 8-row gun; (this step may not be required depending on the substrate) 13 Determine the signal value with a microplate reader; (Note 6) 14 Analysis of results (Note 7) Intimate Note Description - Experience Summary Note1: If it is necessary to reduce the non-specific adsorption of the whole ELISA system reagent on the enzyme label plate during the coating process, it is recommended to select a hydrophobic enzyme plate (polysorp), and the coated antibody concentration should be sufficient 2-5ug/ul. Note 2: The blocking solution does not necessarily have a blocking effect and requires experimental verification (grouping of uncoated antigens). Generally, the smaller the molecular weight, the better the blocking agent. Note3: In the initial stage of method development, the concentration range of the standard curve can be widened from 1000 ng/ml to 0.1 ng/ml. Note4: The dilution of enzyme-linked antibodies requires different dilutions for comparison. For enzyme-linked antibodies with monoclonal antibody components, the same dose curve can be produced for two dilutions of enzyme-linked antibodies, indicating that the enzyme-linked antibody is over-expressed, ELISA There is no deviation in signal transmission. For the enzyme-linked antibody with multi-anti-component, the dilution is judged more complicated. It can be judged whether the concentration of the enzyme-linked antibody is appropriate according to the back-test at the highest concentration of the standard curve. If the higher-concentration two-point signal value of the reference substance is close to , indicating that the concentration of the polyclonal antibody is too low. Note 5: For the absorbance value substrate and the fluorescent substrate, the signal value detected by the instrument is proportional to the color development time, and it is appropriate to control it for 10-30 minutes. It is necessary to confirm the linear range of the signal of the detection instrument in advance. For example, the linear range of the absorbance value of the general microplate reader is 0-3, the absorbance value is non-linear between 3-4, and the control signal value should not exceed when the color is developed. 3, or the point where the signal value is greater than 3 is not included in the fit of the standard curve. Note 6: Different substrates need to be tested with different instruments, absorbance readings, fluorescence readings, and chemiluminescence readings. Pay attention to whether the laboratory's microplate reader has this type of reading function during the substrate selection process. Note 7: The dose curve fitting of the standard curve can be linear, log-linear or four-parameter fit. The test standard is that the back-test deviation of each concentration point of the standard curve is less than 20%. If not, delete the highest concentration point until Standards compliant. V. Summary The linear range of the instrument's detection signal is limited. For example, the linear range of the TMB chromogenic solution is 0-3. The ELISA method development and optimization process is more often used to control and adjust the signal value of the reference to make the signal. The value is in the linear range. Use enhanced TMB color development to extend the color development time, increase the highest concentration point of the standard curve, increase the concentration of enzyme-linked antibodies and other enhanced signal values, and vice versa. In the case of a limited linear range of signal values, it is one of the keys to method sensitivity to eliminate the non-specifically adsorbed signal values ​​as much as possible. Hydrophobic enzyme-labeled plates are used, and smaller molecular weight blocking agents are used, and relatively simple monoclonal antibodies are used. A conjugated antibody or a streptavidin enzyme-linked antibody or the like is a form effective for eliminating a non-specific adsorption signal. The rational selection and matching of diverse reagent consumables during ELISA method development is the key to a stable and sensitive ELISA method, and the understanding of the characteristics of diverse reagent materials is the key to selection, which needs to be based on signals in comparative experiments. The change system is to understand and analyze.  - References - 1. ELISA application overview and methodological development Helps to grasp the principle of ELISA quantitative method development 2. Decker J, Reischl U, Butler JE . SolidSupports in Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Other Solid-Phase Immunosassas [M]// Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. Humana Press, 2004. A very useful ELISA review is useful for a comprehensive understanding of all aspects of ELISA. 3. Desilva B, Smith W, Weiner R, et al. Recommendations for the Bioanalytical Method Validation of Ligand-Binding Assays to Support Pharmacokinetic Assessments of Macromolecules [J]. Pharmaceutical Research (Dordrecht), 2003, 20(11): 1885-1900. The introduction of the method validation process of the ELISA quantitative method system helps to fully evaluate the pros and cons of the ELISA method. 4. Findlay JWA, Dillard RF. Appropriate calibration curvefitting in ligand binding assays [J]. Aaps Journal, 2007, 9(2): E260-E267. A comparative study of the different functions of the ELISA standard curve. 5. Cox KL, Devanarayan V, Kriauciunas A, et al. Immunoassay Methods [J]. 2012. An English lab manual similar to this one can be learned from learning. 6. Pillutla RC . Book review: ligand-binding assays: development, validation and implementation in the drug development arena. [J].Bioanalysis, 2011, 3(3):271-273. A very useful book on all aspects of the ligand-binding assay is useful for deepening learning. Previous article The journey of discovery in the depths of flowers (starting articles) The journey of discovery in the depths of flowers (pH) The journey of discovery in the depths of flowers (centrifugal emulsification) Interpretation of technical specifications for the determination of pH value of cosmetics + experiment! What kind of make-up products can really stand firm in the market? Application of Ohaus ST ion meter in fluoride ion detection of toothpaste Application of MB23 Moisture Analyzer in Daily Chemical Industry Low-key master never shows the dew | Ohaus products Party Want to know about Ohaus's high quality products? Please call the Ohaus sales service line "4008-217-188" and our professional engineers will be happy to help you! China Foldable Stretcher,Medical Rescue Folding Stretcher,Rescue Folding Emergency Stretcher,Emergency Portable Stretcher, we offered that you can trust. Welcome to do business with us. Spine Board,Spine Board Stretcher,First Aid Spine Board,Plastic Spine Board Medton Medical , https://www.medtonmedical.com

This time, the dry goods are full,
Come take a look at the direct method of ELISA in the development of biopharmaceuticals!
ELISA has a wide range of applications in all aspects of biopharmaceutical development:
Quantitative platforming methods using ELISA techniques - generally can be divided into two categories, indirect and direct. 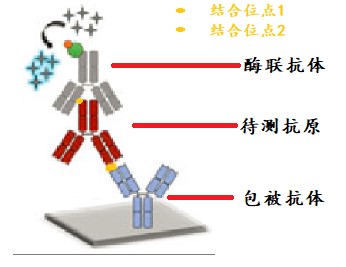
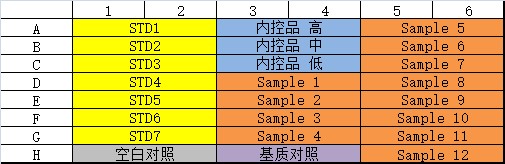
Fourth, ELISA quantitative methodology development actual case analysis
layout 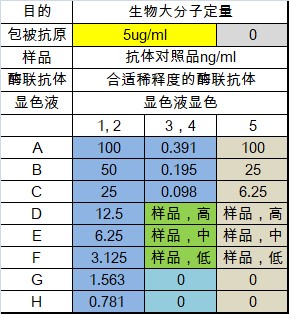



You are engaged in the development of biopharmaceuticals, you must know the ELISA development method | dry goods full!