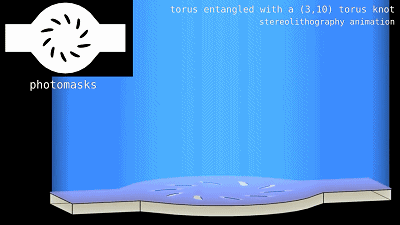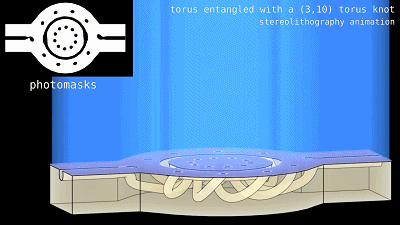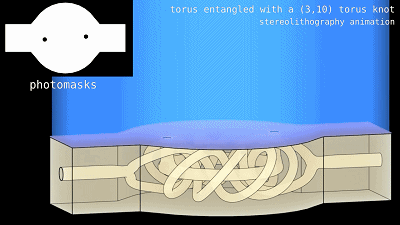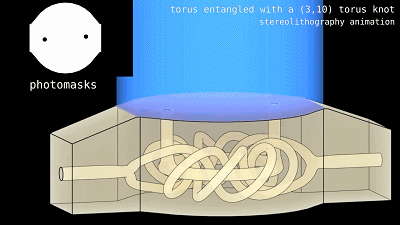
Compared with other repairers, doctors have to repair people, but it is a lot harder. Not to mention the complexity of the human body, there is no spare "parts" alone, which is enough to make people vomit blood. Organs donated by current organ transplants are restricted by rejection and donor sources and are difficult to be widely used. And through the organization of artificial organs, it looks very beautiful, but the reality is very skinny, especially the solid organs such as heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney. The light grows out of the corresponding cells is not finished, you have to have the correct structure to exercise their normal Features. Recently, Bagrat Grigoryan, Kelly Stevens and Jordan Miller of Rice University used 3D lithography technology to bio-compatible hydrogels. 3D printed a lung model containing blood vessels and airways, in which blood oxygen was realized. He also constructed a small piece of liver that survived after transplantation into mice. Related research obtained the Science cover recommendation [1]. Regeneration of organs through tissue engineering, where is broken, can be said to be an ideal of people in medicine, and even some people imagine that by constantly changing organs, the human body becomes a ship of Hughes, to achieve eternal life. In recent years, the hot 3D printing technology has opened a door for the production of organs through tissue engineering, such as tissue engineering auricle cartilage, which has been used from mice to the clinic to repair the outer ear of patients with small ear malformations [2] . However, there is no complicated structure in the outer ear cartilage. Previously, the next generation of 3D printed ovaries was successfully produced, and only a scaffold was printed to put the follicles into the blood vessels. The blood vessels were also implanted by the host after implantation. If such a technique is to be used to generate a solid organ, there is still a lot of difference. The function of the solid organs is inseparable from the complex spatial structure, such as the two chambers and two chambers of the heart, four valves, the hepatic lobules of the liver, the spleen and spleen sinus in the spleen, the blood vessels and airways intertwined in the lungs, The nephron of the kidney, and even the valve that is oriented open in the blood vessels, are essential structures for these organs to function. In order to create these complex structures, the researchers chose three-dimensional lithography to locally polymerize the photosensitive resin by illumination to print a specific structure. Compared to point-to-point printing of traditional inkjet 3D printing, 3D lithography can process millions of voxels simultaneously, supplemented by lemon yellow shading, and the printing efficiency and precision are greatly improved. The light said that the doctor did not practice the fake, the researchers first used a three-dimensional lithography to print a small section of the valved blood vessels, a small test knife. The next step is to challenge the higher difficulty. In the lungs, there are two sets of blood vessels and airways that are entangled with each other and are not interoperable. Can three-dimensional lithography be completed? Dark red anaerobic blood flows in, and bright red oxygen-rich blood flows out. However, the gas exchange in the lungs is not such a tube, it is the alveoli and the surrounding capillary network. In addition to the lungs, the researchers also tried to make a small piece of liver. The activity of the albumin promoter in hydrogel-encapsulated hepatocytes is 60 times higher than that of the single-cell state! At the same time, because the total particle size exceeds the voxel size of tissue engineering 3D lithography, the researchers have also constructed a more advanced carrier to attach these hydrogel-coated liver cells to natural fibrin. Leave a gap as a blood vessel. Subsequently, the researchers implanted human umbilical vein endothelial cells into the space, and then implanted this small piece of "liver" into mice with chronic liver injury. After 14 days, active albumin promoters were still detected in these implanted "liver", and the liver cells survived successfully! Professor Stevens, co-author of the paper, said: "Organic engineering has been struggling for a generation in this area. With this research, we can now better ask, 'If we can print it out, it looks even more like breathing. The organization of our health organizations, so will their functions be more like those organizations? 'This is an important issue, because the quality of the organization will affect its success as a treatment." Source: Singularity Network Lead Xray Blanket 0.5Mmpb,Dental Xray Shielding Blanket,Lead Lined Xray Protection Blanket,Lead Blankets For Patient Longkou Kangxie Medical Instrument Co., Ltd , https://www.lkkangxiemedical.com The paper was recommended by Science cover
The paper was recommended by Science cover 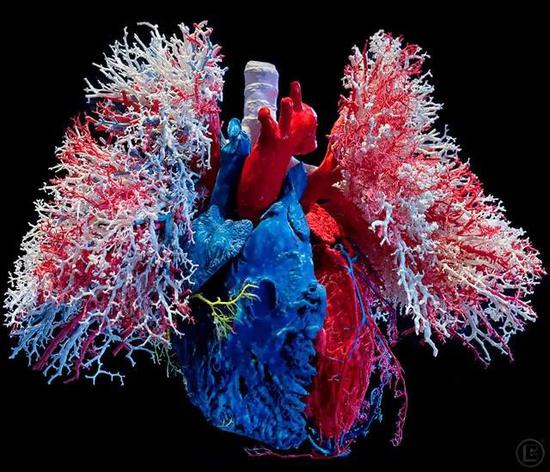 Cardiopulmonary vascular cast
Cardiopulmonary vascular cast 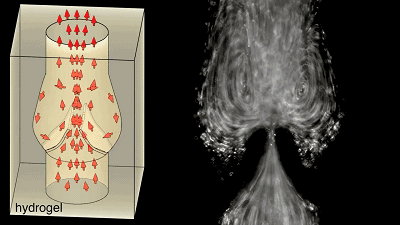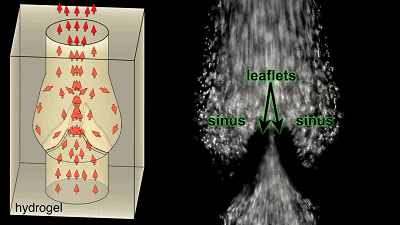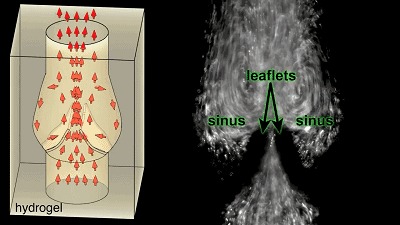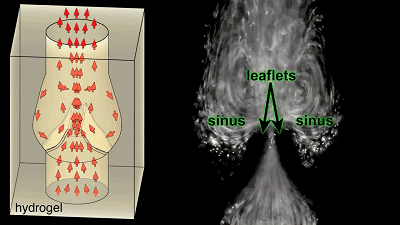 The blood flow flows in one direction along the valve, and the initial attempt is successful, to give yourself a hand!
The blood flow flows in one direction along the valve, and the initial attempt is successful, to give yourself a hand! 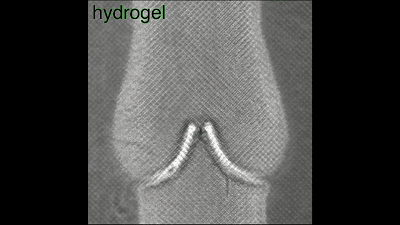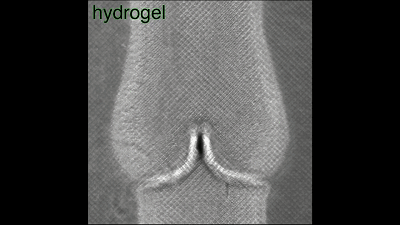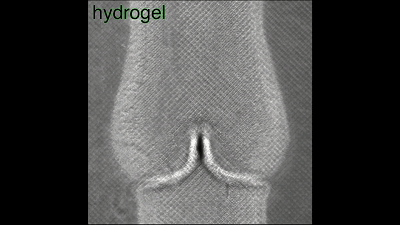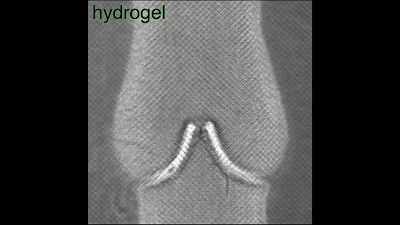
 Fill the liquids of different colors to see each other.
Fill the liquids of different colors to see each other. 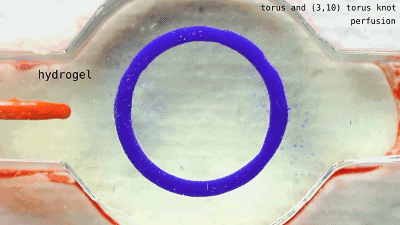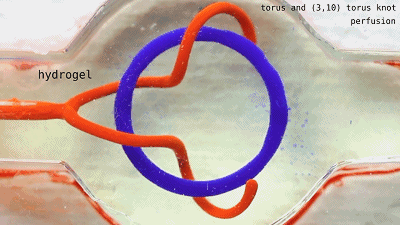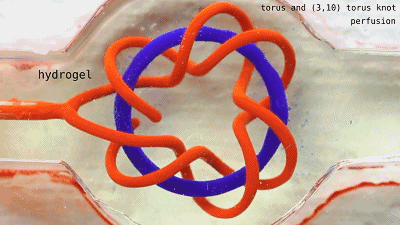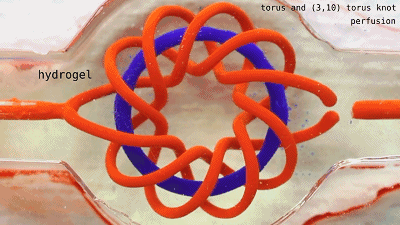 The two sets of non-interconnected pipes seem to be ok, and the next step is oxygenation.
The two sets of non-interconnected pipes seem to be ok, and the next step is oxygenation. 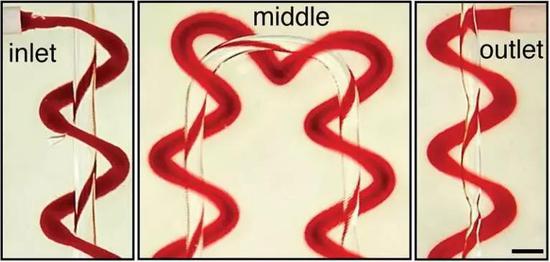
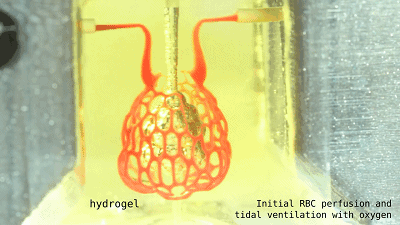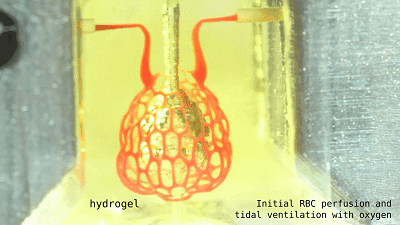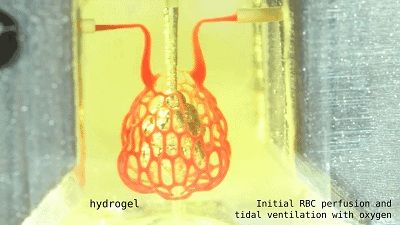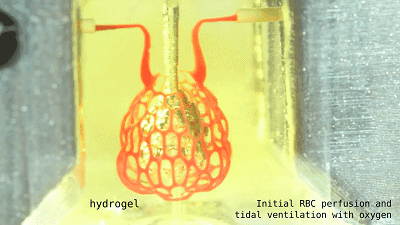 It is a lung that is more assembled with such alveoli.
It is a lung that is more assembled with such alveoli. 
Open up! Scientists first print out the lungs that "breath"
:2019-05-16
Next Article
How to manage after the cultivation of Atractylodes?
Prev Article
Radish cultivation techniques