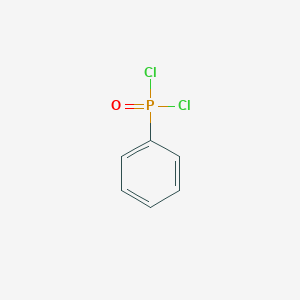
Phenylphosphonic Dichloride CAS No.824-72-6 Phenylphosphonic Dichloride Basic Information
Phenylphosphonic Dichloride Structure
phenylphosphonic dichloride,phenylphosphonic dichloride wiki,phenylphosphonic dichloride msds,phenylphosphonic dichloride reaction,phenylphosphonic acid dichloride ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
During the three years, this “medical reformâ€, which mobilized extensively and sincerely absorbed social forces, has progressed step by step to the core region after experiencing a period of small to large, difficult to follow, and repeated trials. At the same time, the community’s discussion and attention on reforms have never stopped.
The Minister of Health, Chen Hao, is also the deputy head of the State Council's leading group to deepen the reform of the medical and health system. He was the vice president of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a famous medical scientist. He has made breakthrough achievements in hematology and molecular biology. In January 2012, Chen Hao and his collaborators received the "San Jergi Research Innovation Achievement Award" from the National Cancer Research Foundation for their achievements in the study of acute promyelocytic leukemia.
As an "expert-type official" who has worked in the field of medical and scientific research for several decades, Chen Hao is also very much aware of the institutional institutional fallacy. In the middle of 2007, after Chen Xi officially assumed the post of Minister of Health, his first important task was to participate in organizing the implementation of the new medical reform. In the following years, deepening the reform of the health care system was the focus of its work.
In the past three years, what has changed in the field of health care in the “big medical reformâ€? How will the medical reforms in the 12th Five-Year Plan be difficult? In early 2012, Chen Hao accepted an exclusive interview with reporters. “The medical reform has reconstructed and adjusted China’s medical and health service system in a certain sense.†Talking about medical reform, Minister of Health Chen Zhen has deep feelings. With the implementation of various reform tasks in the past three years, the masses “have difficulty in seeing a doctor and expensive to see a doctorâ€. To a certain extent, the health indicators of Chinese residents have entered a period of rapid improvement. On this basis, Chen Hao believes that the continued implementation of the reform of the medical and health system will surely further "let the people share the results of the reform."
The preliminary establishment of the basic medical and health system framework with Chinese characteristics
As of the end of 2011, the new medical reform that will take three years will be completed. 1.27 billion Chinese residents enjoyed extensive coverage of basic medical care. All government-run grassroots medical and health institutions have established basic medicine systems. More than 70% of the districts have county-level hospitals, township hospitals, and community health services that meet the standards.
Looking back at this round of medical reform, people find that this is not a simple reform of medical treatment or medicine, but covers the basic medical insurance system, basic drug system, primary health care system, equalization of basic public health services, and public hospital reform. Systematic sorting and change in aspects. Therefore, in the private sector, this round of medical reform has been given the meaning of “big medical reformâ€.
During the "12th Five-Year Plan" period, reforms in the medical and health field will continue. The liquidation of the debts of China's primary health care institutions is also planned to be completed within two years. The general practitioner system has been approved by the State Council. Doctors' practice of "multiple practice" has gradually begun.
“The medical reform has reconstructed and adjusted China’s medical and health service system in a certain sense. The initial formation of grass-roots medical and health institutions complements the functions of secondary and tertiary hospitals and professional public health agencies, and the linkage between the upper and lower levels, and the parallel efforts of Chinese and Western medical institutions, public and non-public medical institutions. The co-existence and coordinated development of the service structure." Chen Xi told reporters, "This has become the most part of the basic medical and health system with Chinese characteristics."
Reporter: The reform of the medical and health system carried out by the national health system has been in progress for nearly three years. What are the outstanding results achieved in the three years of medical reform? What benefits have the people gained from it?
Chen Hao: In the past three years, the problem of “difficulty in seeing a doctor†has been alleviated to some extent. The situation of backward medical service facilities and weak service capacity in rural and remote areas has changed significantly. The problem of “three shorts and one short†has gradually eased in large urban hospitals, and the people’s medical treatment experience has greatly improved. Within 15 minutes, the proportion of households that can reach medical institutions increased from 80.3% in 2008 to 83.3% in 2011, and rural areas increased from 75.6% to 80.8%.
Urban and rural residents began to enjoy low-level, extensive coverage of basic medical care, and the problem of “expensive to see a doctor†has eased. The proportion of farmers’ participation in medical expenses paid for medicines fell from 73.4% in 2008 to 49.5% in 2011, and the economic burden of medical treatment for doctors and doctors was greatly reduced. According to the Ministry of Health's 2011 medical reform study, the percentage of rural residents who did not visit the hospital for two weeks decreased from 12.4% in 2008 to 6.1% in 2011, and urban residents fell from 6.4% to 4.0%. Calculated at comparable prices, the growth rate of outpatient and inpatient expenses in public hospitals from 2008 to 2011 was controlled within 7%, which slowed down the rapid growth of medical expenses since the mid-1990s.
Looking at the implementation of the reform of the health care system for three years, the national health indicators continue to improve. From 2008 to 2011, the maternal mortality rate dropped from 34.2 per 100,000 to 26.1 per 100,000 and the infant mortality rate dropped from 14.9 到 to 12.1 ‰. With the implementation of various reform tasks, the health indicators of China's residents have entered a period of rapid improvement. This is the greatest benefit to the people.
Reporter: After the new round of medical reform, what is the current situation of China's medical system? Have you basically established a basic medical and health system framework with Chinese characteristics?
Chen Hao: The coverage of China's basic medical security system has reached more than 95%. A developing country with a population of 1.3 billion has achieved such success in less than 10 years and is hailed as a miracle of the world by the international community. The basic drug system has also made phased progress. World Health Organization experts believe that no other country can start such a large-scale drug system reform in such a short period of time.
In a certain sense, medical reform restructured and adjusted China's medical and health service system. The initial formation of grass-roots medical and health institutions and the second- and third-tier hospitals, professional public health agencies complement each other, up and down linkage, Chinese and Western medicine institutions pay equal attention to both public and non-public medical institutions co-exist, coordinated development of the service landscape, become the most basic health system With Chinese characteristics.
The equalization of basic public health services has made our country’s long-standing policy of “prevention oriented†have institutional arrangements. This is a prominent highlight of medical reform.
It can be said that after several years of hard work, China’s basic medical and health system framework has been initially established and has become an important part of the socialist system with Chinese characteristics. It will not only contribute to the long-term benefit of people’s health, but also explore the Chinese-style medical reform. Solution.
Reporter: With the implementation of various medical reform tasks, have structural problems that have long plagued the scientific development of the health industry been improved?
Chen Hao: China's health industry is undergoing structural changes. This is the effect of the reforms that we hope to see over the years.
The first is the more significant change in the allocation of health resources. The problems of heavy urban and rural areas, heavy emphasis on medical care, emphasis on high-end lightness, and emphasis on Western medicine, medicine, and traditional Chinese medicine are being reversed, and the orientation role of public financial investment in grassroots, rural, and public health has been steadily increasing. Second, the people’s health service utilization structure began to change. The masses have more recognized and trusted grassroots health services and their use of services has grown.
In addition, the gap in health development between urban and rural areas and regions in China gradually narrows. The survey shows that in 2003, the proportion of urban and rural residents enjoying medical security in China was 55% and 21%, respectively. Towns were significantly higher than rural areas. In 2011, this proportion increased to 89% and 97%, respectively, and rural areas surpassed towns and cities. The above progress shows that the speed of the coordinated development of urban and rural medical and health care is accelerating, and the long-standing urban-rural dual structure and regional health differences are undergoing profound changes.
Reporter: Has the people's problem of “expensive to see a doctor†have improved during the “11th Five-Year Plan†period, especially during the implementation of medical reform in the past three years? How do you evaluate the role of health care reform in macroeconomic and social sustainable development?
Chen Hao: In recent years, major structural changes have taken place in China's total health expenditure. In 2001, the proportion of personal health expenditure in China's total health expenditure was as high as 60%, and government budgetary health expenditure and social health expenditure accounted for only 16% and 24% respectively. The proportion of personal health expenditure in 2010 decreased to 35.5%, and the proportion of government budget and social health expenditure rose to 28.6% and 35.9% respectively. This major structural change shows that the structure of health financing in China tends to be reasonable, the burden on residents is relatively reduced, and fairness is significantly improved.
Looking at the medical reform from a more macroscopic perspective, we have found that medical reform also plays an important role in the sustainable development of the macro economy. Medical reform establishes a safety net for people to seek treatment for the disease, relieves the worries of the masses, expands immediate consumption and furthers domestic demand; healthcare reform creates more jobs and opportunities; promotes the development of national economy-related industries, and drives the growth of manufacturing and service industries. Promote technological progress and product innovation. All these have made important contributions to building a socialist harmonious society and enhancing the country’s soft power. At the same time, health financing and service systems with Chinese characteristics, evaluation systems for health economics, and health evidence-based decision-making mechanisms have gradually matured in their efforts to explore, reflecting our country’s public service and social management from theory to practice in the field of people’s livelihood. Major innovations.
All in all, the three-year reform practice and results have fully demonstrated that the objectives, directions, and principles of China's medical reform established by the Party Central Committee and the State Council are correct, policies and measures are feasible, are in line with the laws of health development, are in line with China’s national conditions, and are consistent with the people. Desire. I believe that these major changes will greatly inspire the confidence of medical reform workers and deepen medical reforms.
"Twelve Five" Medical Reform
After completing basic reforms and achieving successes in medical reforms, the two major problems of “difficulty in accessing patients and expensive medical care†have been controlled to a certain extent. The “big medical reform†has begun to recur to the core regions, and the difficult problems have also emerged. The adjustments and the concentrated exposure of institutional conflicts have further increased the difficulty and complexity of reforms.
Price reform has become a top priority. “We must make a choice. Is it an unreasonable mechanism to continue to maintain, or is it determined to eliminate the use of medicine to supplement the doctor?†Chen said that during the “12th Five-Year Plan†period, it strived to steadily and systematically eliminate “drugs for medicine†during the “12th Five-Year Plan†period. "Disadvantages.
Reporter: What are the new characteristics of the internal and external environment for deepening medical reform during the 12th Five-Year Plan period?
Chen Hao: From the perspective of the internal and external environment in the health field, the first is the rapid economic development, rapid changes in the way of life, accelerated aging of the population, and the transformation of disease patterns, which has brought heavy burden of infectious and non-communicable diseases to our residents; With the improvement of the social security medical system and the living standards of residents, the expectation for health and medical and health care services is even higher. Third, China’s medical and health undertakings generally lag behind social and economic development, and its internal structure as an important social service industry is not always reasonable. The scale, function, structure, and service model of the health industry are not yet fully prepared to meet the above challenges.
From the perspective of medical reform itself, reforms have entered deep-water areas and the institutional mechanisms have become more and more contradictory. First, the imbalance in the allocation of health resources still exists, especially the shortage of quality resources, which still cannot meet the basic medical and health service needs of the people; second, the reform of deep-level institutional mechanisms is advancing relatively slowly, and changes in the way of health development are also recognized and practiced. It is necessary to continuously explore; Third, the progress of reforms in various regions is uneven, and some key links have not yet made breakthroughs. There is still a gap between the effectiveness of medical reform and social expectations.
At the same time, we must also see that the “12th Five-Year Plan†period is still a period of strategic opportunities for deepening medical reforms, and it still has a favorable political environment, material conditions, social atmosphere, and mass base that promote the healthy development of health care reform and health care. This is at all levels. The strong leadership of the party committee and government, the active cooperation of various departments, the ever-increasing economic strength, the people's understanding and support, and the successful experience accumulated during the three years of medical reform. We must understand the situation, seize the opportunity, advance with difficulty, meet new challenges, and win new medical reforms.
Reporter: How will the medical reforms during the 12th Five-Year Plan be difficult? What are the most important institutional malady in the current medical and health field?
Chen Yun: The most urgent need at this time is to “make up for medicineâ€. This mechanism has promoted the irrational rise in medical expenses, caused the abuse of drugs, distorted the behavior of medical personnel, and eroded our health team and must be completely eradicated.
For a long time, medical and health institutions have indeed relied on medicine to supplement medical services to maintain their operation and development. At present, pharmaceutical income is still an important channel for compensation. Reforming medicine for medicine must inevitably touch the real interests of medical and health units. We must make choices. Will we continue to maintain this unreasonable mechanism or will we make up our mind to eliminate medicine? In order to safeguard the interests of the public, for the healthy development of the health care industry, and for the long-term construction of the health team, this mechanism will sooner or later be changed. It is much more advantageous and much more beneficial to change now and thoroughly than change in the future.
The health administrative departments in all localities must actively strive for government leadership in accordance with the deployment and requirements of the “12th five-year plan†medical reform, strive to create conditions, implement the cancellation of the relevant policies for drug supplementation, give full play to the role of medical insurance compensation, and steadily push forward with price reforms. During the second five-year period, the system was steadily and steadily removed from the abuse of medicine. Relevant reforms The 300 pilot counties in this year pushed ahead first and strived to implement them in county-level hospitals in 2013. In 2015, all public hospitals were fully promoted.
Reporter: Some experts believe that the combination of the project-based payment system and medicine supplementation is the root cause of big prescriptions and indiscriminate examinations. Will the payment system reform be comprehensively promoted during the 12th Five-Year Plan period?
Chen Hao: During the "12th Five-Year Plan" period, the reform of the payment system should be regarded as the key to the reform of the institutional mechanism and vigorously promoted.
According to international experience, the payment system is an important means for medical insurance institutions to control costs. With the full coverage of the basic medical insurance system in China, the conditions for the reform of the payment system have matured. Health administrative departments should give full play to their advantages of managing new rural cooperatives and managing services, and take the lead in advancing the reform of the payment system of the new rural cooperative medical system. At the same time, it is necessary to coordinate with other relevant departments such as medical insurance and commodity prices, and pay close attention to summarizing the pilot experiences in recent years in various regions, formulating implementation plans, and determining the payment methods for adapting to different levels of medical institutions and different types of services, using total amount advance payment, disease type, and service unit. , According to the payment method of the first person instead of paying according to the project. We must combine the clinical pathway with the reform of the payment system, do basic work such as cost measurement, and ensure that the reform and cancellation of the payment system are promoted simultaneously with medicine and medicine.
Solve the "expensive"
Looking back at the path of medical reform in the past three years, from the experimentation and promotion of the basic drug system to the comprehensive reform of the primary health care institutions, medical reform has basically followed the medical reform principle of “guarantee basic, strong grassroots, and construction mechanismsâ€.
While completing the comprehensive reform of primary health care institutions, the people, especially the grassroots, have become increasingly prominent. During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, the Ministry of Health will focus on promoting the risk protection mechanism, critical illness protection, and basic medical insurance system of the New Rural Cooperatives, and seek solutions to this problem.
Reporter: Serious diseases often lead to high medical expenses that families cannot afford.
How will the “12th Five-Year†period reduce the risk of the people, especially farmers, getting sick and returning to poverty due to illness?
Chen Hao: We must strengthen the risk protection mechanism of the new rural cooperative medical system and rationally establish a management system. New rural cooperative cooperation is a basic medical security system for rural residents and has achieved wide coverage. During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, as the level of fundraising continues to increase, it is necessary to regard enhancing the protection of farmers’ health risks as an important point for consolidating and improving the system, and on the basis of generally increasing the level of participation of farmers, make effective institutional arrangements and establish stable Serious disease protection mechanisms.
At present, exploration of the integration of the basic medical insurance system for urban and rural residents is under way in some places, which inevitably involves the basic medical insurance management system. Aligning the insurance system and service provision management under the general health system is conducive to the realization of lean, uniform, and efficient principles and cost control; however, considering the current management situation and the integration of the system, the related management department can also implement unified management and integration. Department office" form. The integration of the basic medical insurance system for urban and rural residents and the adjustment of the management system are of great importance. It is necessary to scientifically demonstrate and make decisions cautiously at the provincial government level and obtain the consent of the competent authorities of the State Council.
Judging from the basic national conditions, most regions should follow the division of responsibilities assigned by the State Council to maintain the existing management system and maintain the stable operation of the system.
Reporter: How will we consolidate and improve the new mechanism for the operation of primary health care institutions in the future to ensure that the grassroots network is not broken?
Chen Hao: We must continue to adhere to the basic principle of “guarantee the basics, strengthen the grassroots, and build the mechanism,†and continue to consolidate the achievements of the comprehensive reform of urban and rural grassroots medical and health institutions.
In 2012, all regions must carry out a “review†campaign on comprehensive grass-roots reforms, conduct a comprehensive inspection on the implementation of policies, measures, tasks, and work goals at all levels, identify weak links, and make it clear that further improvement of grass-roots medical institutions will be implemented in the coming years. The key tasks and policy measures for running the new mechanism. We must effectively consolidate the implementation of the basic drug system, seize key links such as implementation of investment policies, standardization of procurement and supply, and strict zero margin sales, and promote the implementation of the basic drug system in the primary and secondary health care institutions in urban and rural areas.
The key period of 2012 medical reform
Reporter: The task of reform in the "12th Five-Year Plan" medical and health field is still heavy. In 2012, it was a crucial year for the "Twelfth Five-Year Plan". How do you think that this year should implement the tasks of annual reforms and create a good "12th Five-Year Plan" for medical reform?
Chen Hao: First of all, we must continue to improve the level of new rural cooperative medical care. Consolidation of coverage, raised the standard of funding to around 300 yuan per capita, the proportion of hospitalization expenses within the scope of the policy reimbursement reached about 75%, the maximum payment limit is not less than 8 times the annual per capita income of farmers, and not less than 60,000 yuan. General outpatient co-ordination. The establishment of a special disease protection fund will increase the coverage of diseases. Promote the reform of payment methods. Exploring and improving the level of the new rural cooperative co-ordination and commercial insurance institutions participating in the handling of services. We will improve the new rural cooperative management operation mechanism, improve services, and safeguard the safety of the fund.
Second, we must consolidate and improve comprehensive reforms at the grass-roots level. Organize a comprehensive "review" campaign at grassroots medical and health institutions. We will improve the multi-channel compensation mechanism, implement government investment, implement the general medical treatment fee system, and give play to the role of the medical security system. We will promote the reform of the personnel distribution system and implement a performance-based wage system. We will implement the Outline of the Basic Rural Health Development Plan (2011-2020). Promote the development of community health services in small and medium-sized cities and promote the general practitioner team service model.
Again, continue to improve the national essential medicine system. Further expand the scope of system implementation. Develop the 2012 edition of the basic drug list and regulate the local addition of non-catalogue drugs. We will standardize the procurement of essential drugs, improve the comprehensive evaluation index system for pharmaceutical companies and drug quality, and do a good job in rural and remote areas. For the exclusive varieties of essential medicines, shortage of varieties, and children's pharmaceutical products, trials have been conducted in the country for uniform pricing and fixed-point production. Formulate basic drug use management methods and gradually standardize its dosage forms, specifications and packaging. Put forward policies that encourage the preferential use of essential medicines. Constantly improve the monitoring and evaluation system for essential drugs.
Finally, we actively promoted the reform of public hospitals. Strengthen the assessment and evaluation of the reform pilot cities, and strive to form an experience that can be promoted to the whole country. It was determined that about 300 counties (cities) promoted the comprehensive reform of county-level hospitals. Strengthen the capacity building of county hospitals and continue to implement counterpart support work. Strengthen the planning and management of medical institutions. Accelerate the establishment of a division of labor and cooperation mechanism between public hospitals and grassroots institutions. We will improve the personnel distribution system in public hospitals and continue to promote the practice of doctors. Continue to implement quality care services, appointments for treatment, convenience clinics and other benefits. The implementation of clinical path management, strict cost accounting, and control of unreasonable growth in medical expenses. Carry out hospital assessment and evaluation.
In addition, we will also promote the gradual equalization of basic public health services. Do a good job in basic and major public health service projects in the country. We will improve the basic public health service project management system and increase the central government's assessment of localities. We will improve the division and collaboration mechanism between primary health care institutions and professional public health institutions to improve the quality of basic public health services. Comprehensively evaluate the implementation of major public health service projects, promote new projects such as health supervision and management services, and study and formulate new cycle project implementation plans.
Reporter: Will the reforms to promote healthy competition in medical institutions further promote the formation of a diversified medical pattern?
Chen Hao: The diversified pattern of medical treatment is conducive to meeting the different levels of the needs of the people, promoting competition, improving efficiency, and controlling costs. We must implement various policies that encourage social capital to provide medical services. We must give priority to social capital by adding new medical service resources, and treat them equally in terms of policies and management, and encourage social capital to organize non-profit medical institutions.
Reporter: With regard to centralized procurement of medicines related to people's drug burden, how will the next step be promoted?
Chen Hao: Centralized procurement of drugs is a key link in the production, distribution, price, and use of drugs. We must constantly improve the procurement of drugs for centralized bidding. During the “Twelfth Five-Year Plan†period, it is necessary to improve the system and advance it in an all-round manner on the basis of summarizing the past experience in bidding and drug procurement. It is necessary to unify the drug procurement platform and unified procurement methods and implement quality priority, integration of research and development, and linking quantity and price. It is necessary to gradually incorporate supplies and equipment procurement into the scope of centralized tender procurement. For some patented drugs, high-value consumables, large-scale equipment exploration for domestic and foreign manufacturers centralized procurement. The centralized procurement of imported products based on international price-based pricing is implemented.
Reporter: The talent issue is the bottleneck of health reform and development. How will the Ministry of Health, while advancing medical reform, innovate the talent training mechanism?
Chen Hao: In the three years since the medical reform, he has done a lot of explorations on innovative personnel training methods and incentives for medical personnel. He has achieved positive results and accumulated valuable experience. To further improve the medical education system. It is necessary to increase the training of general practitioners and continuously increase the number of general practitioners so that every community health service center and township health center have at least one general practitioner. To establish and implement a residency training system. We must innovate the training and use mechanisms for grassroots personnel, establish a system of special doctors, and increase the scale of free training for order orientation. To meet the requirements of health reform and development, we will vigorously cultivate all kinds of shortage-qualified personnel and high-level medical teaching and research talents such as nursing, public health, traditional Chinese medicine, pharmacy, and health management.
During the "12th Five-Year Plan" period, we must also innovate the distribution of incentives for medical personnel. In combination with the reform of public institutions, a pay system that meets the characteristics of the medical and health industry must be established to improve the income distribution mechanism that embodies the value of medical labor and improve the overall income level of medical personnel. Expand the scope of job performance wages. Implement post management to achieve equal pay for same work. Increase the proportion of hospital personnel expenditures to business expenses. The balance of hospital revenues and expenditures is focused on improving the treatment of medical personnel.
Product Name: Phenylphosphonic dichloride
CAS: 824-72-6
MF: C6H5Cl2OP
MW: 194.98
EINECS: 212-534-3
Mol File: 824-72-6.mol
Melting point 3 °C(lit.)
Boiling point 258 °C(lit.)
density 1.375 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
refractive index n20/D 1.559(lit.)
storage temp. 2-8°C
solubility Miscible with benzene, chloroform, dimethyl sulfoxide and carbon tetrachloride.
form Liquid
color Clear yellow to brown
Specific Gravity 1.394 (25℃)
Water Solubility reacts
Chen Wei, Ministry of Health: Medical reforms need to be replaced by medicines
It has been nearly three years since the Chinese health system implemented the reform of the medical and health system. This reform is related to the well-being of the 1.3 billion Chinese people.
Next Article
Micro vacuum pump selection skills
Prev Article
Breeding and breeding of golden pheasant